Discover ETAC’s design considerations for custom dry-type transformers, including core materials, winding configurations, and safety standards.
August 7th, 2024
Custom dry-type transformers are essential components in various applications, offering the flexibility to meet specific requirements and constraints of diverse projects. At ETAC Service & Supply, our custom dry-type transformers are designed with a focus on performance, reliability, and efficiency. This article will highlight crucial design considerations such as core material selection, winding configurations, winding materials, insulation systems, cooling methods, enclosure types, and safety standards, with a special focus on CSA C9.
To explore dry type transformer components in action, view our dry type transformer product line designed for industrial and utility needs.


The core material plays a pivotal role in the performance and efficiency of dry-type transformers. At ETAC, we carefully select core materials to ensure optimal functionality:
Selecting the appropriate core material is critical as it directly impacts the transformer’s performance, efficiency, and cost.
The choice of winding configuration depends on factors such as the voltage and current ratings, cooling requirements, and mechanical stress considerations.
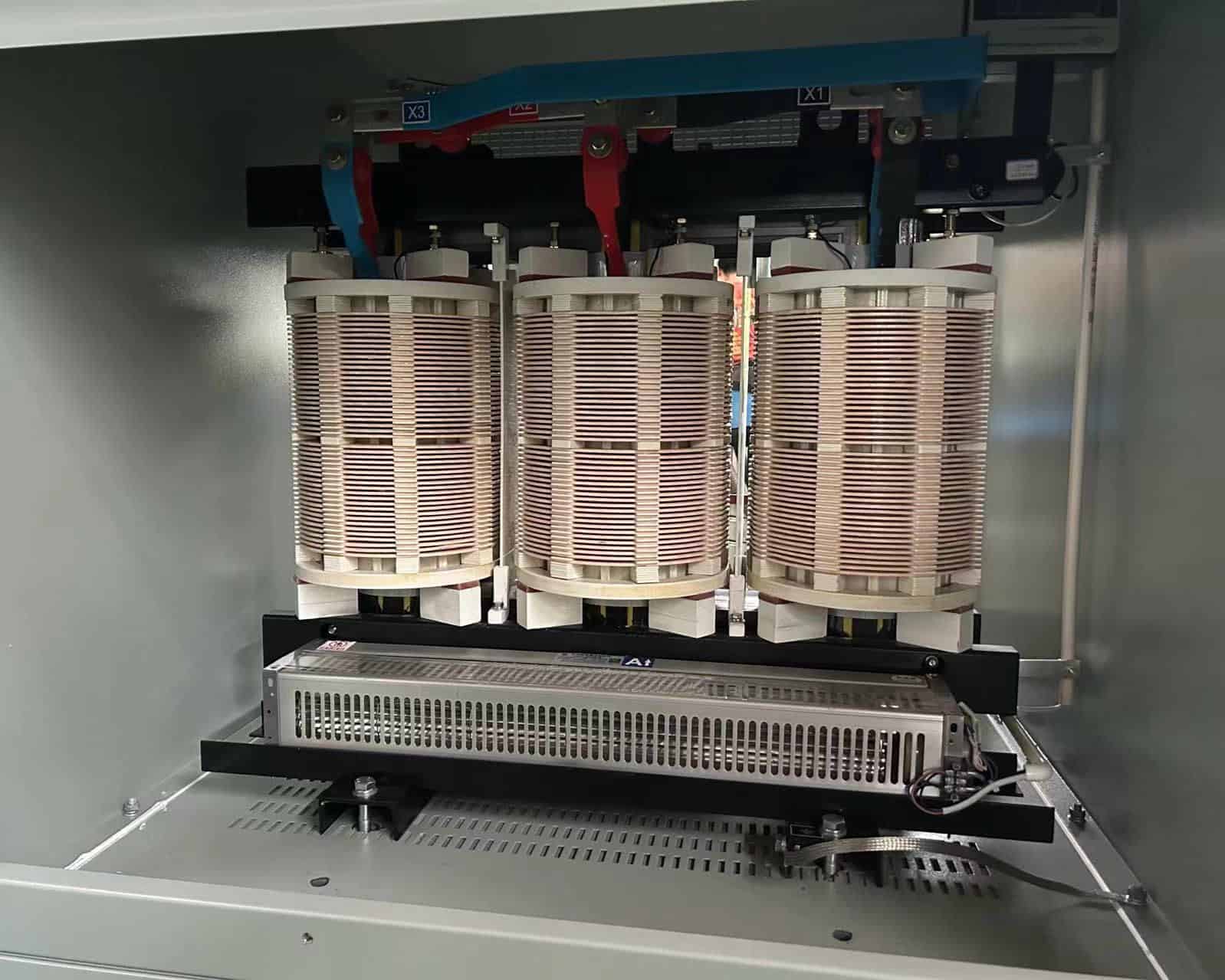
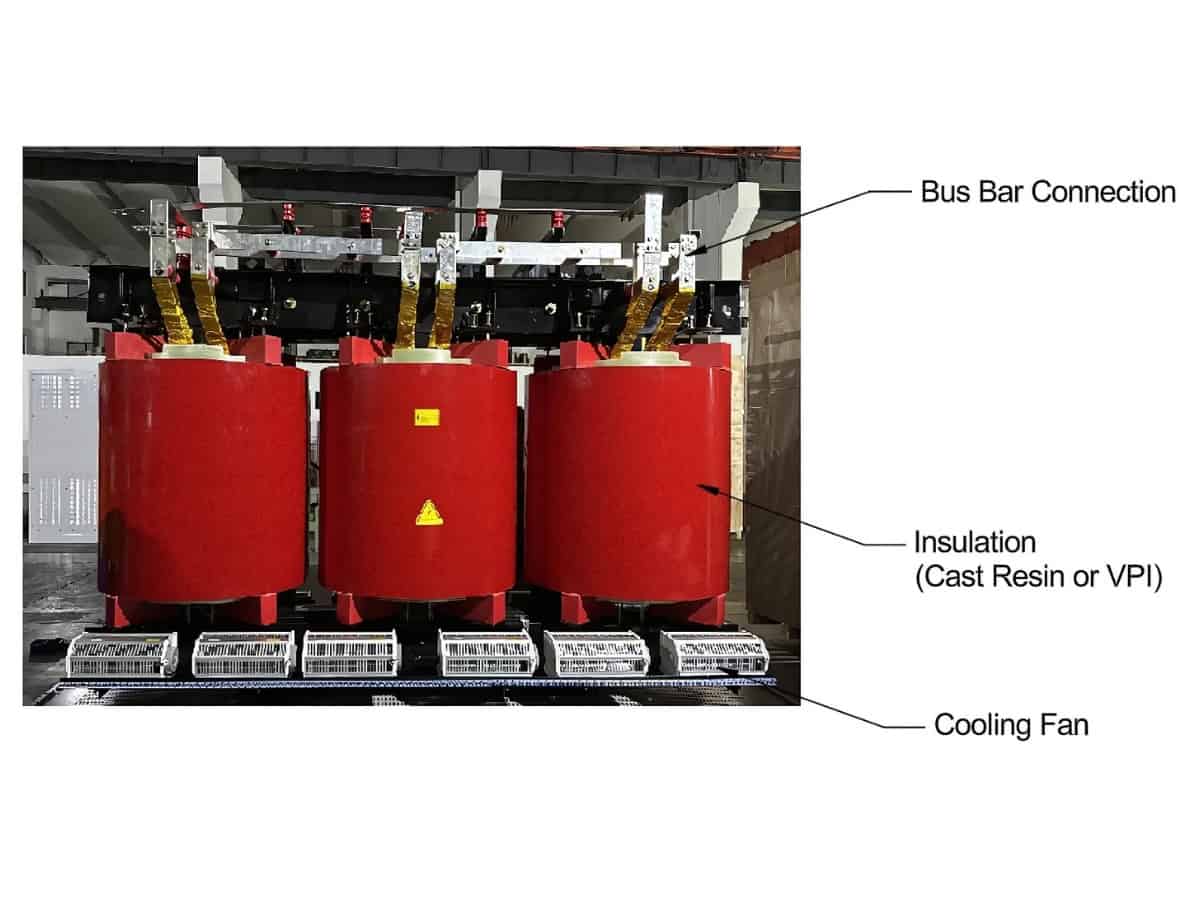

Choosing the right winding material involves balancing cost, efficiency, mechanical strength, and application-specific requirements.
As we reviewed core material selection, winding configurations, and winding materials, we understood their crucial role in dry-type transformer performance and efficiency. However, dry-type transformers involve more than these aspects. In Part 2, we’ll explore insulation systems, cooling methods, enclosure types, and adherence to safety standards like CSA C9.